I am Yuheng Ji (冀昱衡), a lyric poet, and a PhD candidate at the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASIA). I am supervised by Prof. Xiaolong Zheng. My research interests include embodied AI and foundation models.
I am also open to collaborative opportunities and research partnerships, feel free to email me: jiyuheng2023@ia.ac.cn.
Email / Google Scholar / Poetry Anthology
🔥 News
- 2026.02: 🎉 Three papers were accepted by CVPR 2026! Congratulations to all collaborators!
- 2026.01: 🔥 Released RoboBrain 2.5 (core contributor).
- 2025.10: 🔥 Released more advanced RoboOS-NeXT (first author).
- 2025.09: 🎉 Reason-RFT accepted to NeurIPS 2025 (first author).
- 2025.06: 🎉 Released RoboBrain 2.0 and RoboOS in BAAI Conference 2025 (first author, core contributor).
- 2025.04: 🌍 RoboBrain 1.0 selected for CVPR 2025’s official Embodied AI Trends Commentary.
- 2025.02: 🎉 RoboBrain 1.0 accepted to CVPR 2025 (first author).
🧭 Research Framework
My long-term aspiration is to build embodied agents with strong real-world generalization, so they can become productive forces in society and benefit all people equitably.
The roadmap is a tightly coupled loop: Evaluation & Analysis informs the design of both methods and models; Method Development empowers Model Construction; model behavior and performance, in turn, validate and refine methods; together, methods and models support System Expansion toward scalable multi-agent intelligence.
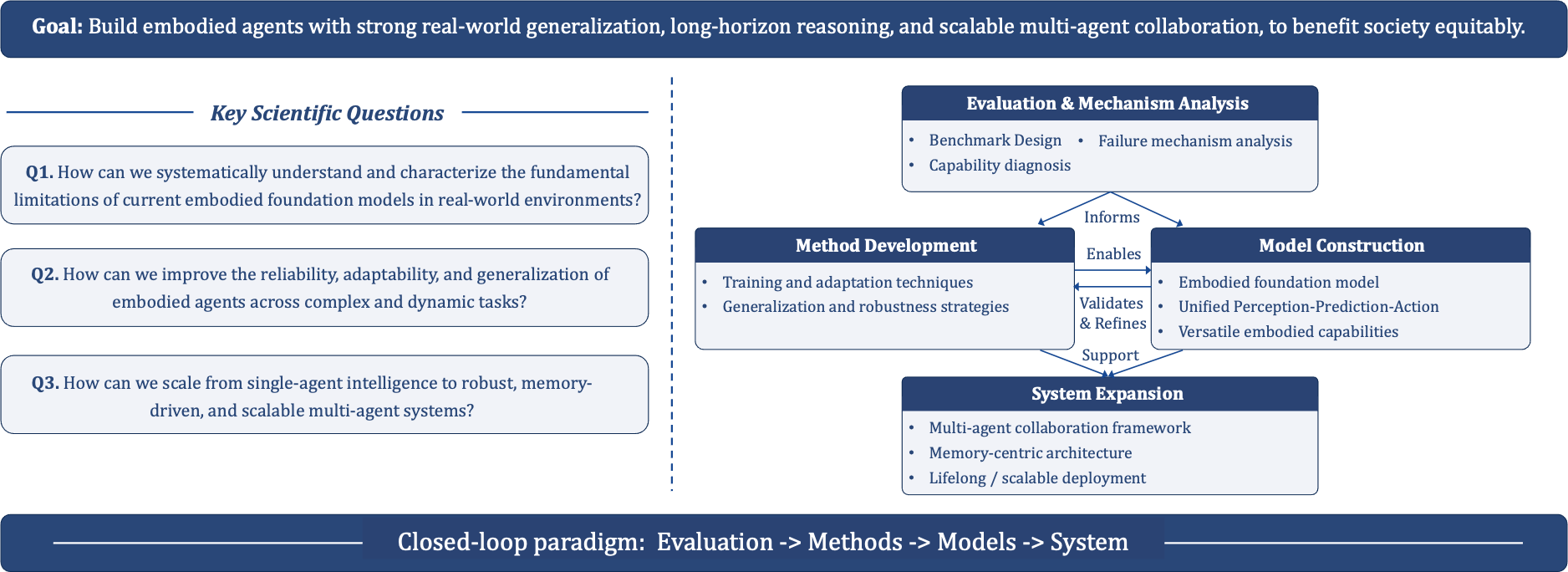
1) Evaluation & Mechanism Analysis
This direction focuses on diagnosing what current models can and cannot do under real-world complexity, including spatial perception, temporal reasoning, and robustness under distribution shifts. The goal is to provide reliable evidence and design principles for downstream methods and models.
2) Method Development
This direction develops training and adaptation methods that improve reasoning quality and action reliability, especially for long-horizon embodied tasks. Typical themes include reinforcement learning, process-level rewards, and stronger intermediate reasoning representations.
3) Model Construction
This direction builds embodied foundation models that unify perception, reasoning, and planning. A key target is to obtain robust spatial-temporal cognition and practical decision-making ability in cluttered, dynamic, and multi-step environments.
4) System Expansion
This direction extends single-agent intelligence to scalable systems, including memory-centric architectures, multi-agent collaboration, and lifelong operation. The objective is to support deployment-ready embodied systems rather than isolated benchmarks.
📝 Publications
Use the left-to-right menu below to browse detailed publications by category.
In the Model Construction module, we were among the early works (CVPR 2025) to formulate embodied foundation models under a Brain+Cerebellum hierarchical architecture. The core distinction between embodied and general foundation models lies in whether abstract human intents (e.g., “I am thirsty”) can be transformed into concrete control signals, such as subtask planning, affordance grounding, trajectory generation, and point-level action targets. As a core contributor, I have been deeply involved in developing the RoboBrain series.
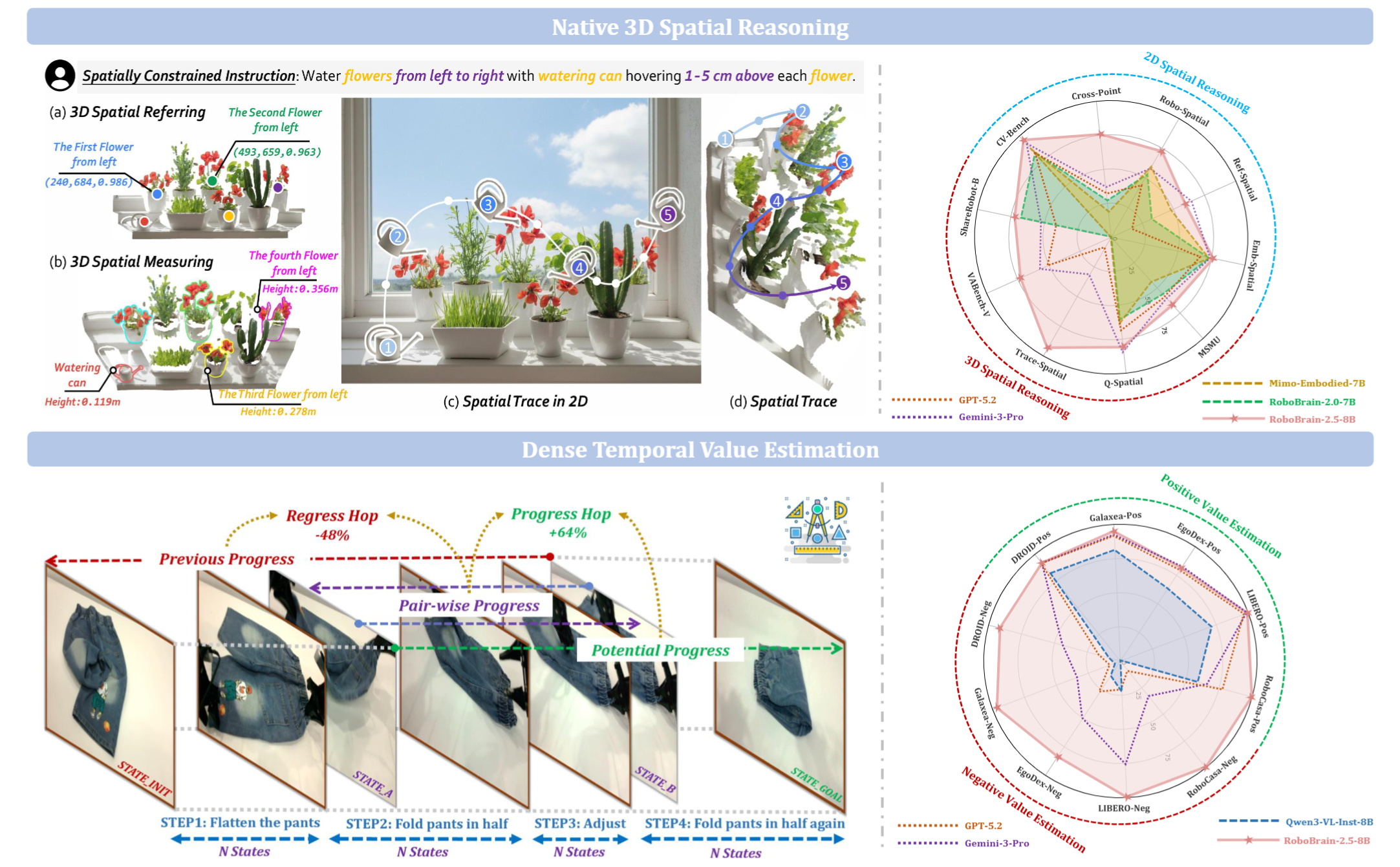
RoboBrain 2.5: Depth in Sight, Time in Mind.
BAAI RoboBrain Team
Core Contributor, Technical Report 2026
Project | Paper | Code 
RoboBrain 2.5 upgrades embodied intelligence along two key axes: depth-aware 3D spatial reasoning and dense temporal value estimation. It predicts physically grounded 3D manipulation traces and step-aware progress signals across viewpoints, improving fine-grained manipulation planning and execution feedback.
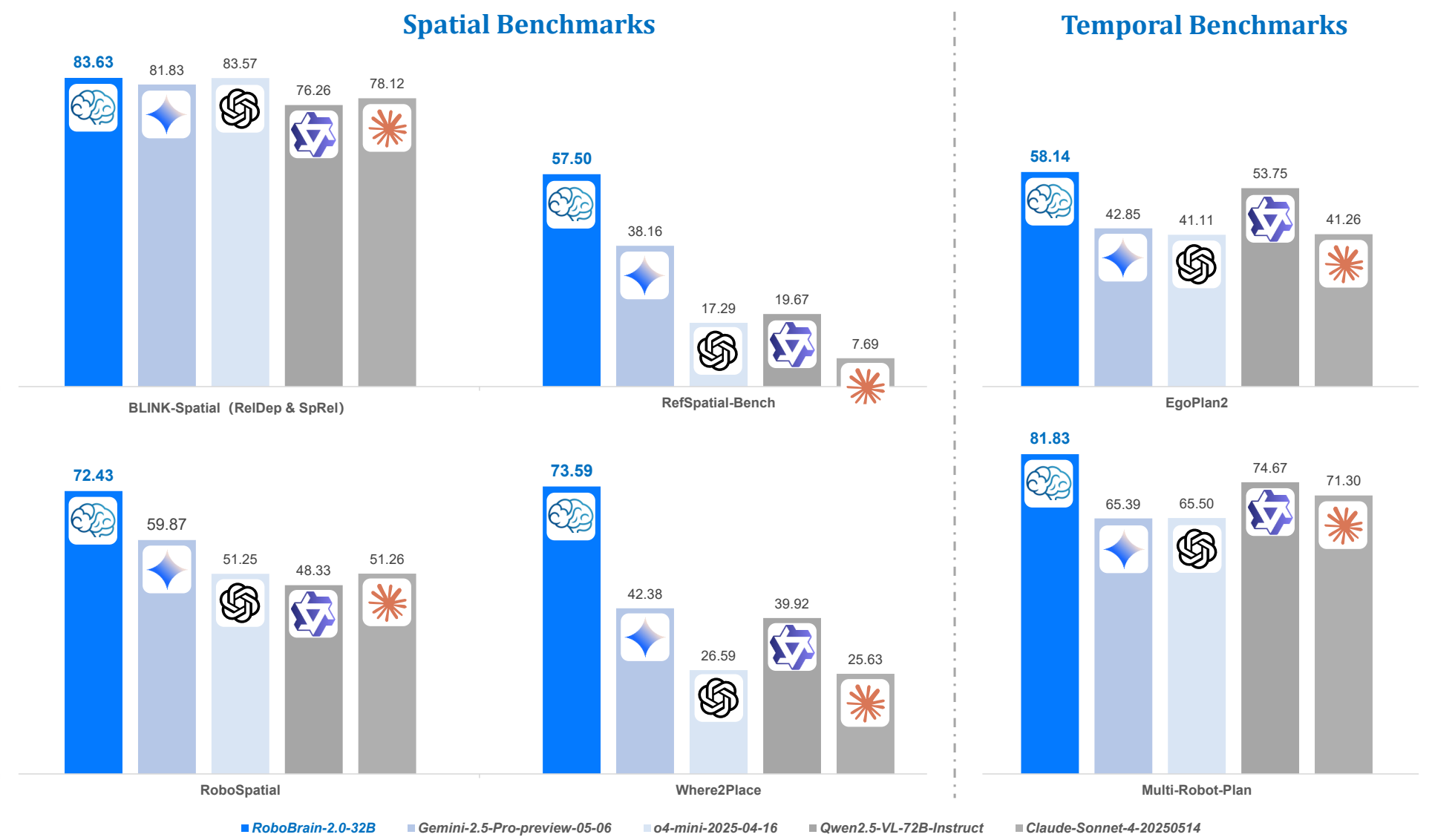
RoboBrain 2.0: See Better. Think Harder. Do Smarter.
BAAI RoboBrain Team
First Author, Core Contributor, Technical Report 2025
Project | Paper | Code 
RoboBrain 2.0 is an embodied vision-language foundation model family with 7B and 32B variants, designed to unify perception, reasoning, and planning for complex physical-world tasks. The 32B model reports leading performance on both spatial and temporal embodied benchmarks, with strong capabilities in affordance prediction, spatial referring, trajectory forecasting, closed-loop interaction, and multi-agent long-horizon planning.
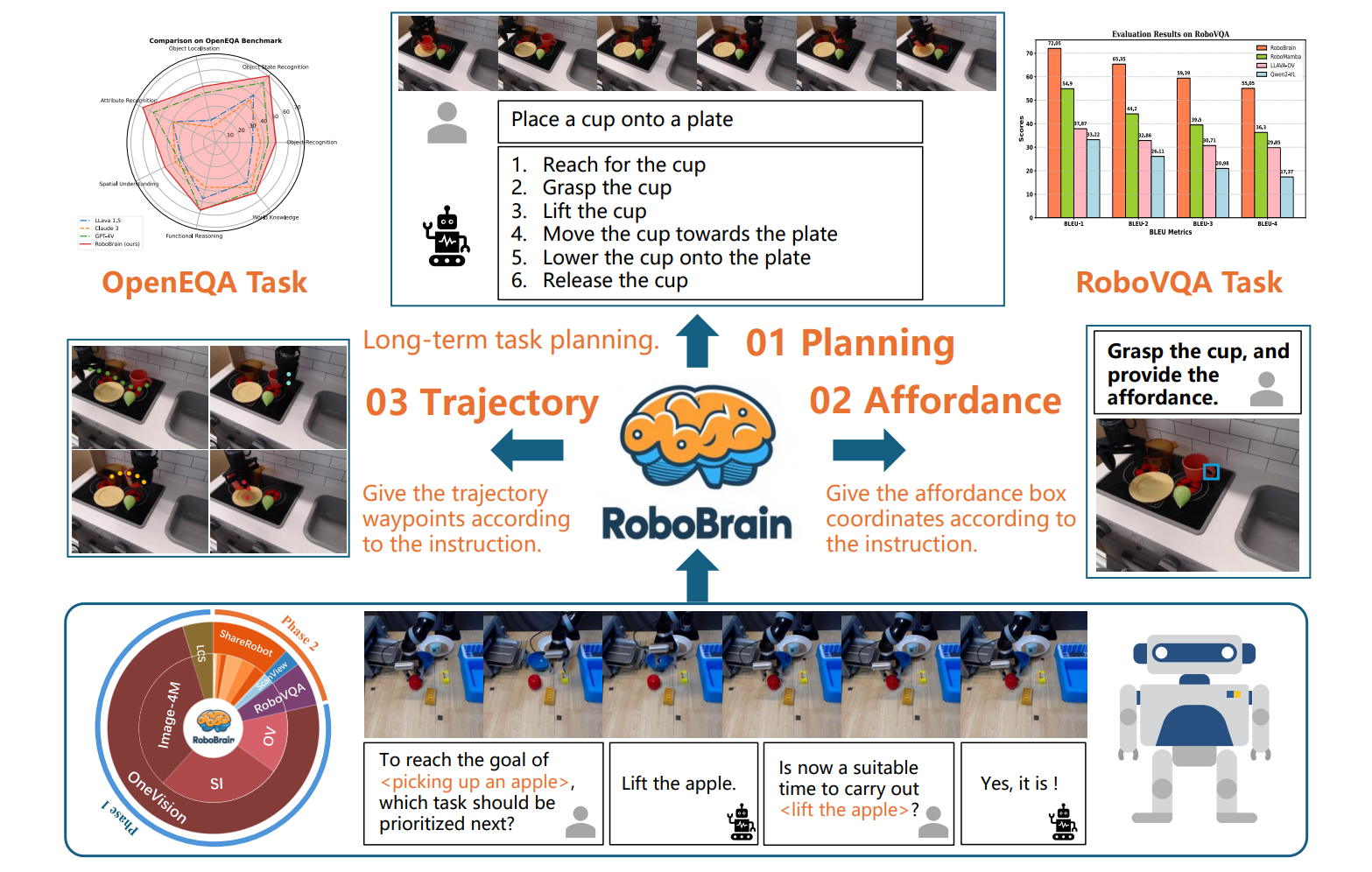
RoboBrain: A Unified Brain Model for Robotic Manipulation from Abstract to Concrete
Yuheng Ji*, Huajie Tan*, Jiayu Shi*, Xiaoshuai Hao*, Yuan Zhang, Hengyuan Zhang, Pengwei Wang, Mengdi Zhao, Yao Mu, Pengju An, Xinda Xue, Qinghang Su, Huaihai Lyu, Xiaolong Zheng, Jiaming Liu, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
First Author, CVPR 2025
Project | Paper | Code 
We developed RoboBrain, a VLM-based model that combines robotic and general multi-modal data, utilizes a multi-stage training strategy, and incorporates long videos and high-resolution images to improve its robotic manipulation capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RoboBrain achieves SOTA performance across various robotic tasks, highlighting its potential to advance robotic brain capabilities.
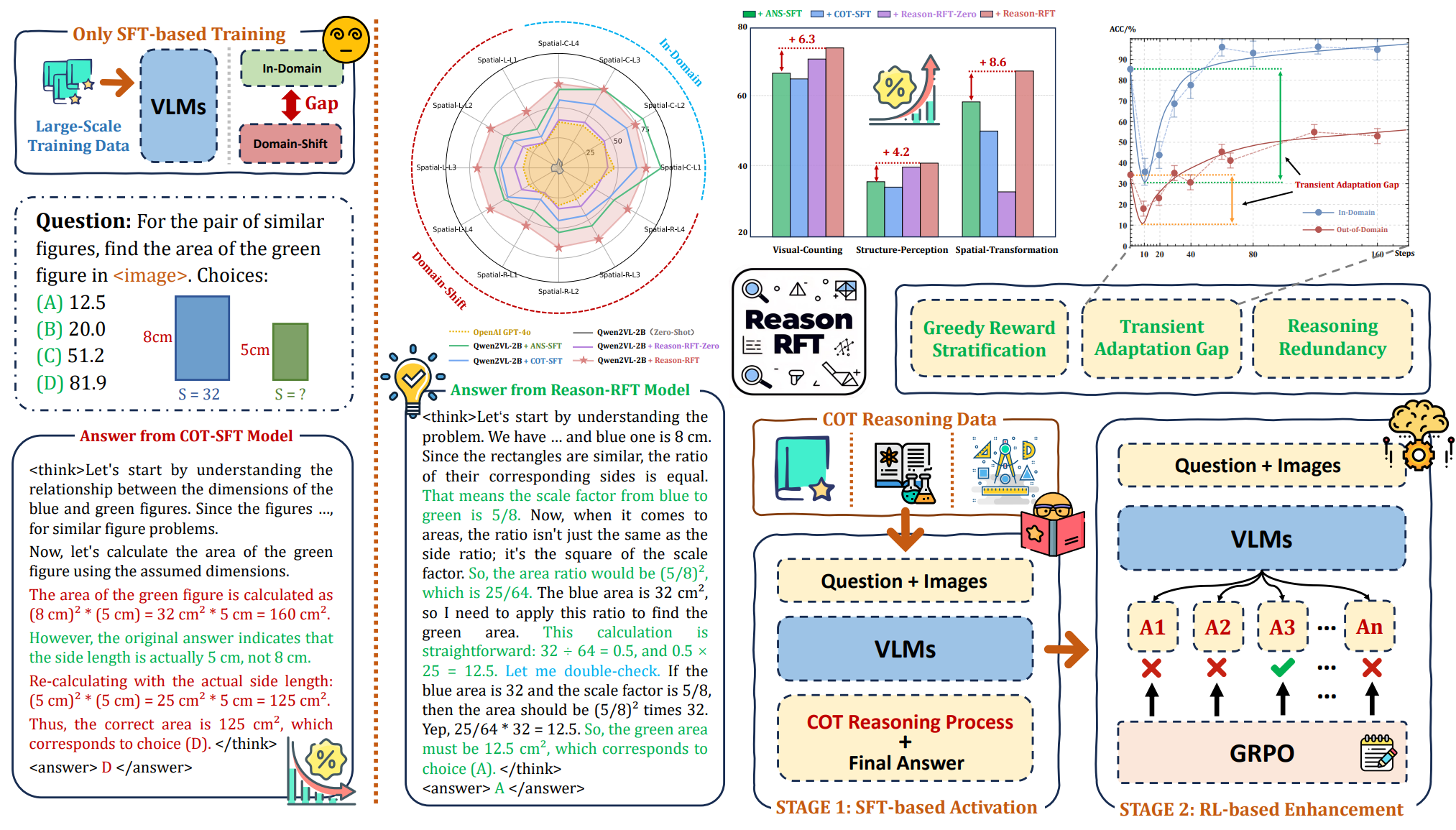
Reason-RFT: Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Visual Reasoning of Vision Language Models
Huajie Tan*, Yuheng Ji*, Xiaoshuai Hao*, Minglan Lin, Pengwei Wang, Shanghang Zhang
First Author, NeurIPS 2025
Project | Paper | Code | Checkpoints | Datasets
We developed Reason-RFT, a reinforcement fine-tuning framework that enhances visual reasoning capabilities in vision-language models. Reason-RFT employs a two-phase training strategy: (1) SFT with curated CoT data to activate reasoning potential, followed by (2) GRPO-based reinforcement learning to generate diverse reasoning-response pairs.
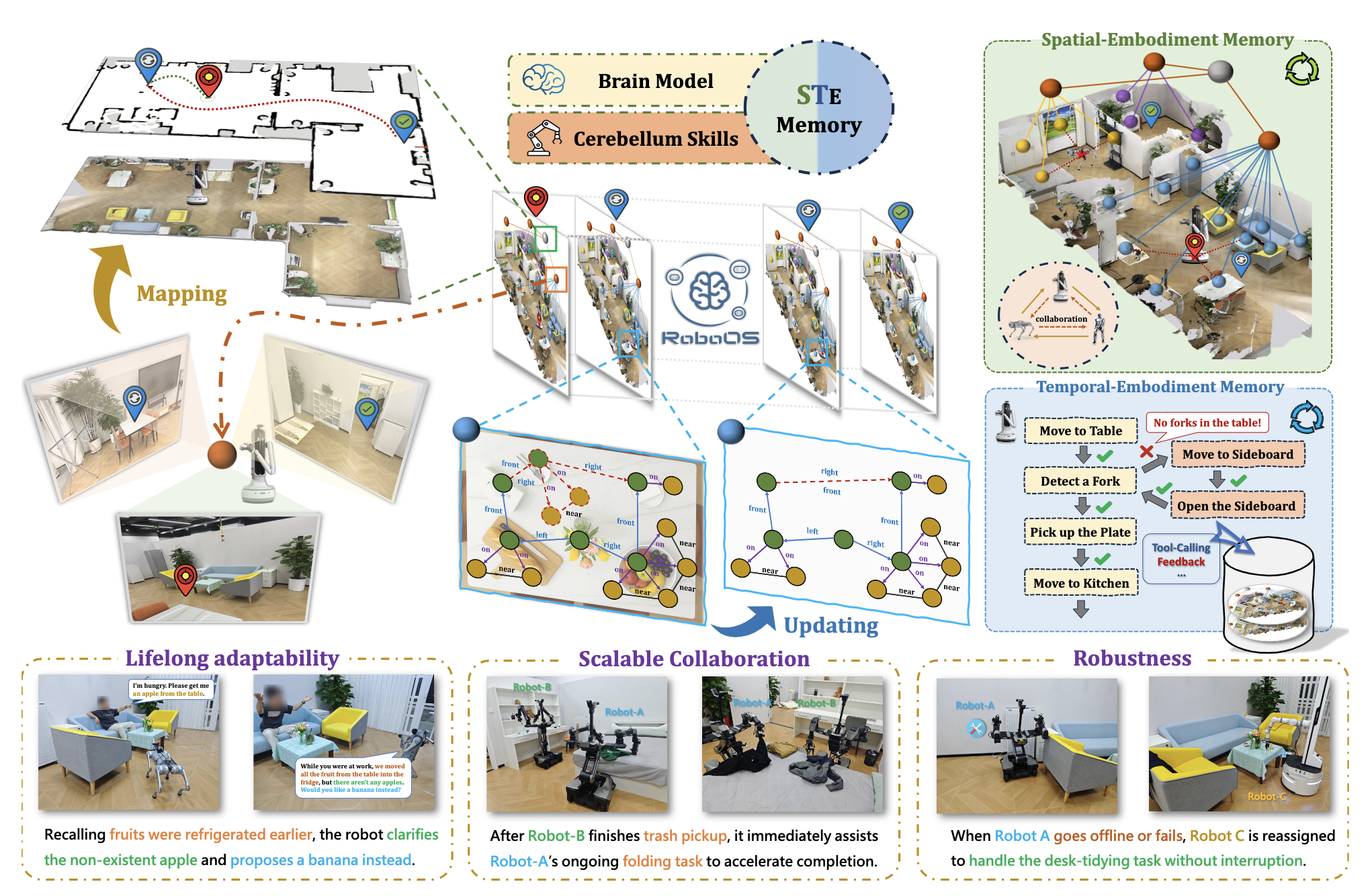
Huajie Tan*, Yuheng Ji*, Cheng Chi*, Xiansheng Chen*, Zhongxia Zhao, Xiaoshuai Hao, Yaoxu Lyu, Mingyu Cao, Junkai Zhao, Huaihai Lyu, Enshen Zhou, Ning Chen, Yankai Fu, Cheng Peng, Wei Guo, Dong Liang, Zhuo Chen, Mengsi Lyu, Chenrui He, Yulong Ao, Yonghua Lin, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
First Author, ArXiv 2025
We present RoboOS, a unified memory-based framework for multi-robot collaboration. At its core, the Spatio-Temporal–Embodiment Memory (STEM) integrates spatial, temporal, and embodiment information to support long-horizon learning, heterogeneous coordination, and fault recovery. Experiments in diverse tasks show RoboOS enables lifelong, scalable, and robust collaboration.
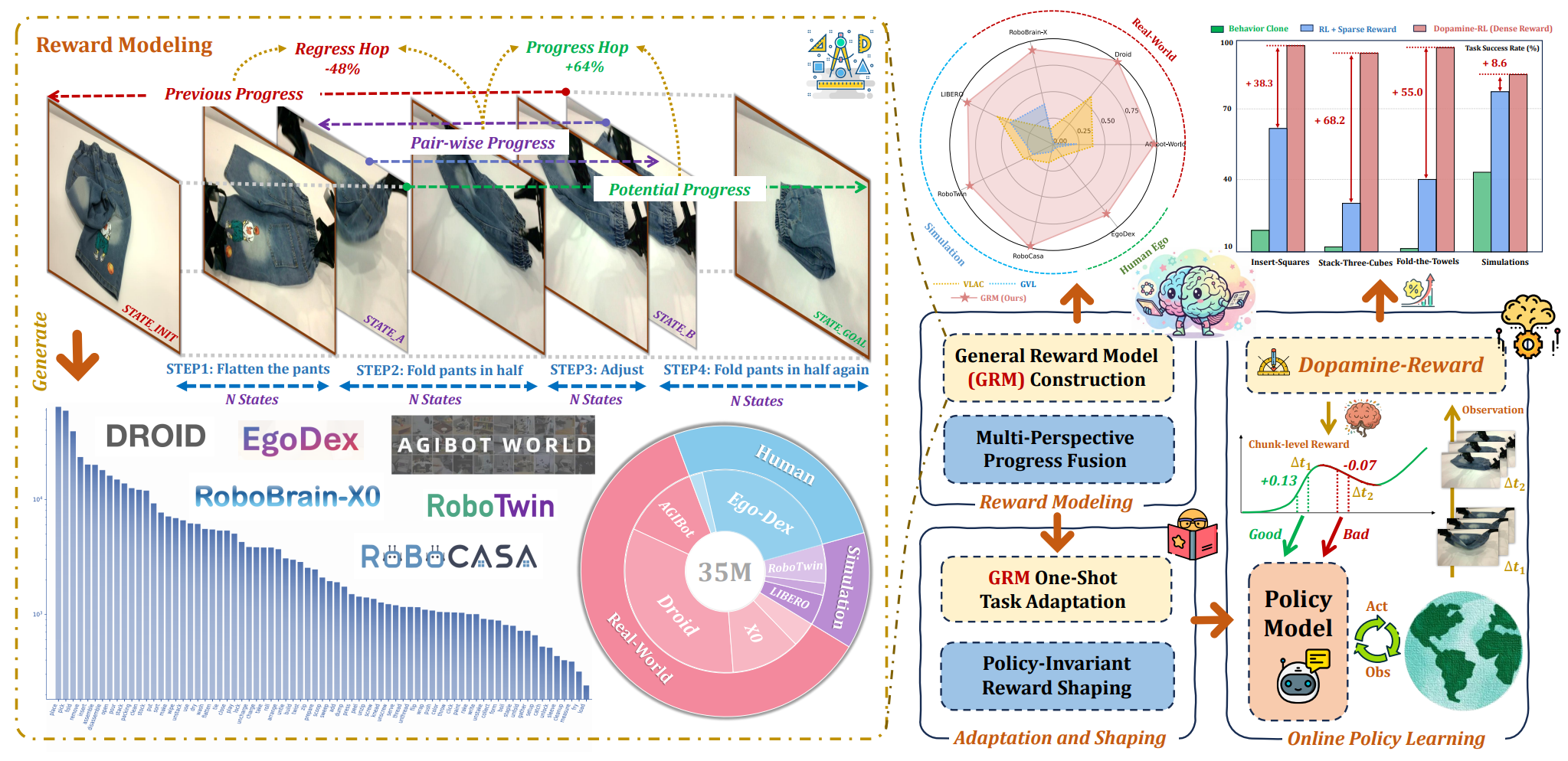
Robo-Dopamine: General Process Reward Modeling for High-Precision Robotic Manipulation
Huajie Tan*, Sixiang Chen*, Yijie Xu*, Zixiao Wang, Yuheng Ji, Cheng Chi, Yaoxu Lyu, Zhongxia Zhao, Xiansheng Chen, Peterson Co, Shaoxuan Xie, Guocai Yao, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
CVPR 2026
Project | Paper | Code 
Robo-Dopamine introduces a step-aware multi-view reward modeling framework (Dopamine-Reward) and a policy-invariant shaping strategy (Dopamine-RL) for robotic RL. The method improves reward assessment quality and substantially boosts online policy learning efficiency on both simulated and real-world manipulation tasks.
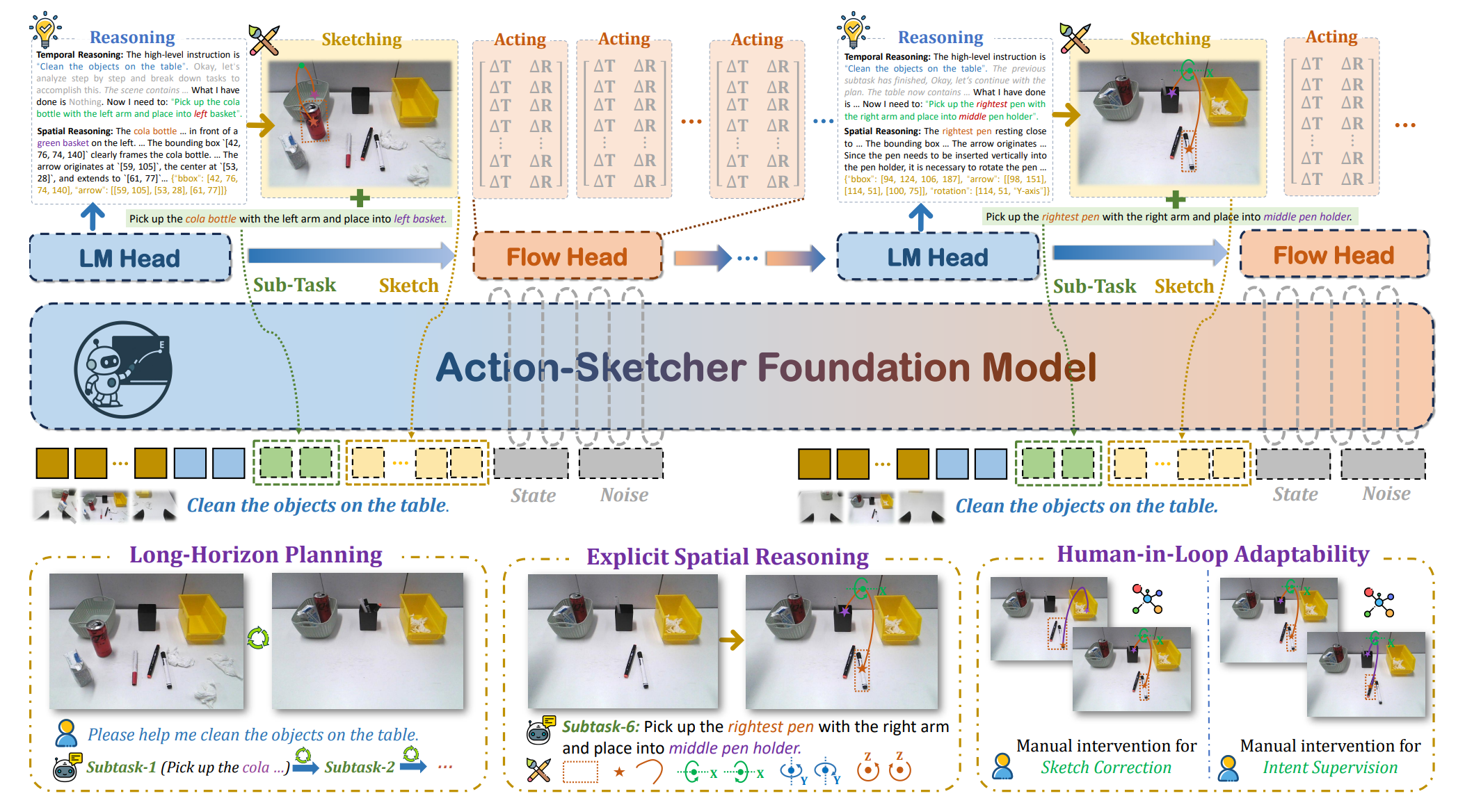
Action-Sketcher: From Reasoning to Action via Visual Sketches for Long-Horizon Robotic Manipulation
Huajie Tan*, Peterson Co*, Yijie Xu*, Shanyu Rong, Yuheng Ji, Cheng Chi, Xiansheng Chen, Qiongyu Zhang, Zhongxia Zhao, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang
CVPR 2026
Action-Sketcher proposes a See-Think-Sketch-Act loop that inserts editable visual sketches as an intermediate representation between language reasoning and robot actions. This design improves grounding, long-horizon robustness, and interpretability in cluttered and dynamic manipulation environments.
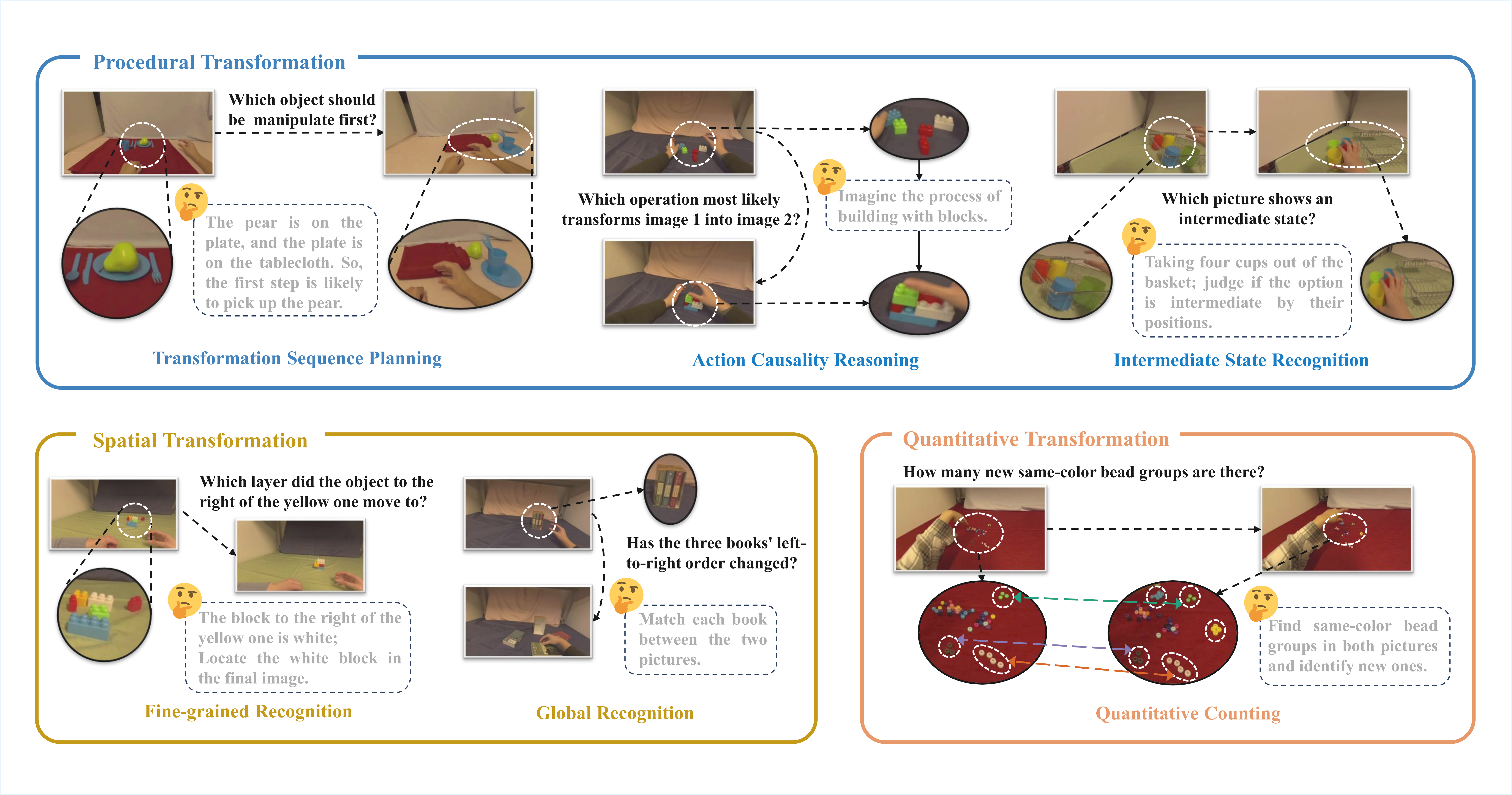
VisualTrans: A Benchmark for Real-World Visual Transformation Reasoning
Yuheng Ji*, Yipu Wang*, Yuyang Liu, Xiaoshuai Hao, Yue Liu, Yuting Zhao, Huaihai Lyu, Xiaolong Zheng
First Author, ArXiv 2025
VisualTrans is the first real-world benchmark for Visual Transformation Reasoning (VTR), evaluating spatial, procedural and quantitative reasoning across 12 human-object interaction tasks. While current models perform well on static tasks, they show significant limitations in dynamic, multi-step reasoning, revealing critical gaps in temporal and causal understanding for intelligent systems.
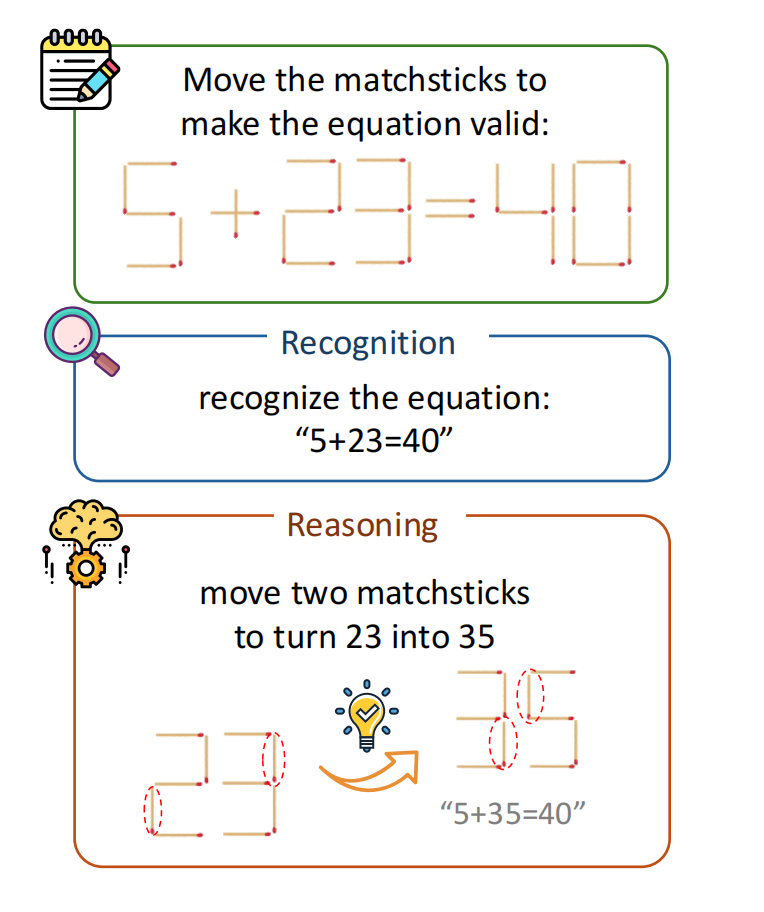
MathSticks: A Benchmark for Visual Symbolic Compositional Reasoning with Matchstick Puzzles
Yuheng Ji*, Huajie Tan*, Cheng Chi*, Yijie Xu, Yuting Zhao, Enshen Zhou, Huaihai Lyu, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Shanghang Zhang, Xiaolong Zheng
First Author, NeurIPS MATH-AI Workshop 2025
MathSticks is a benchmark for Visual Symbolic Compositional Reasoning (VSCR) that unifies visual perception, symbolic manipulation, and arithmetic consistency. Each task presents an incorrect matchstick equation in a seven-segment style. The goal is to move exactly one or two sticks—under strict stick-conservation and digit-legibility constraints—to make the equation mathematically correct.
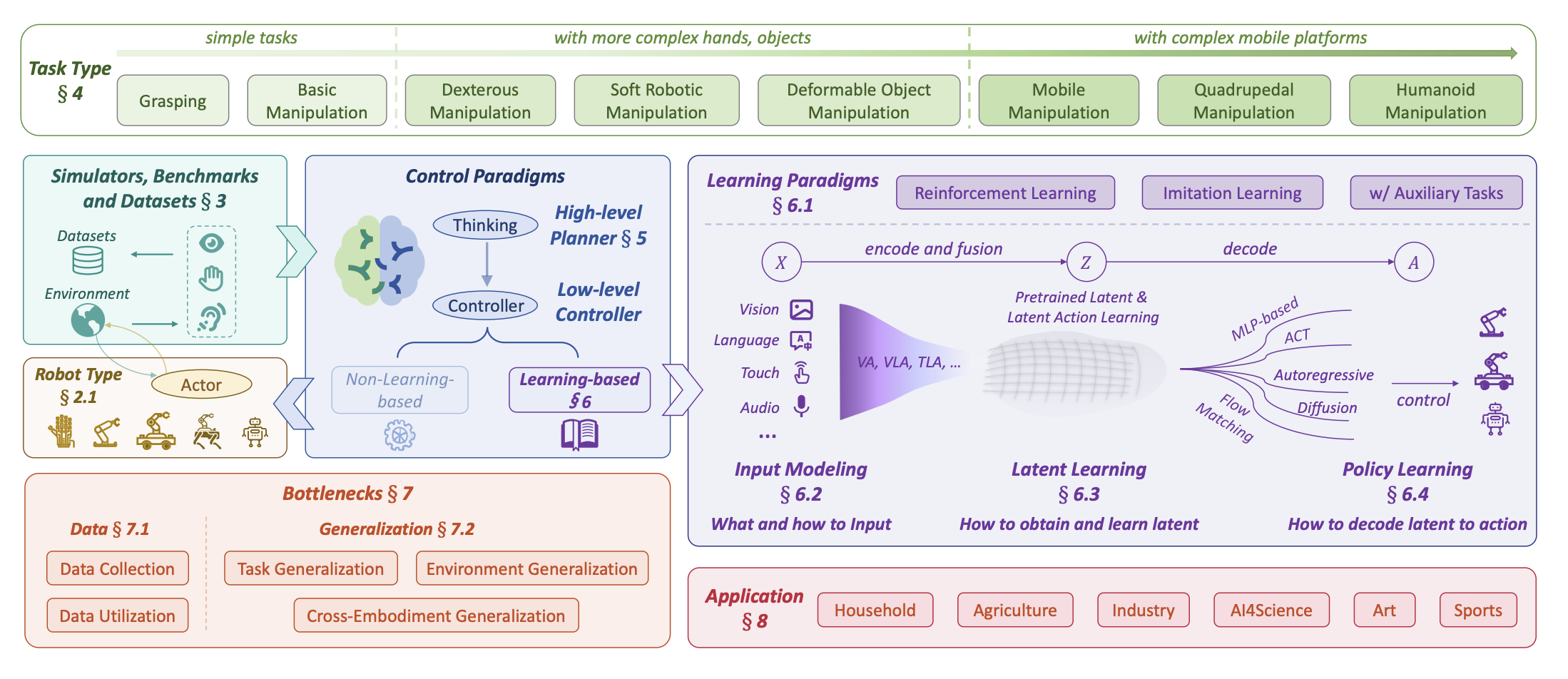
Towards a Unified Understanding of Robot Manipulation: A Comprehensive Survey
Shuanghao Bai, Wenxuan Song, Jiayi Chen, Yuheng Ji, Zhide Zhong, Jin Ynag, Han Zhao, Wanqi Zhou, Wei Zhao, Zhe Li, Pengxiang Ding, Cheng Chi, Haoang Li, Chang Xu, Xiaolong Zheng, Donglin Wang, Shanghang Zhang, Badong Chen
ArXiv 2025
Synthesizing over 1200+ publications, this survey restructures the landscape of robotic manipulation with a unified taxonomy for planning and control. We also provide the first systematic dissection of the key bottlenecks—data, utilization, and generalization—poised to define the next era of progress.

Zirui Song*, Guangxian Ouyang*, Mingzhe Li, Yuheng Ji, Chenxi Wang, Zixiang Xu, Zeyu Zhang, Xiaoqing Zhang, Qian Jiang, Zhenhao Chen, Zhongzhi Li, Rui Yan, Xiuying Chen
AAAI 2026
VLMs enhance robotic manipulation but rely on costly annotated data, limiting OOD adaptability. We propose ManipLVM-R1, a RL framework with verifiable rewards (RLVR), replacing supervision to optimize task outcomes for better generalization. Two rule-based rewards drive physical reasoning, achieving strong performance on fewer data and OOD scenarios.
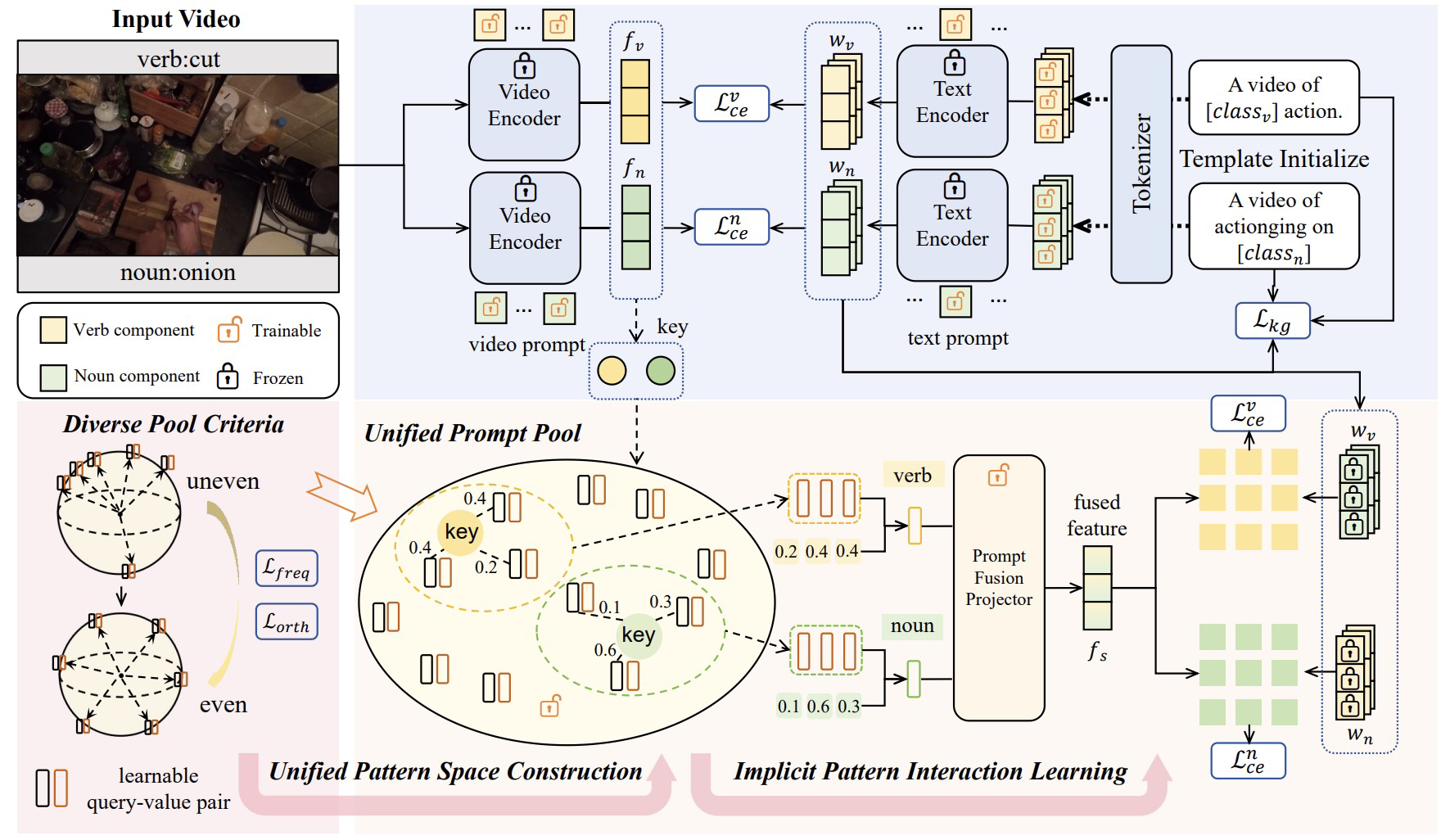
EgoPrompt: Prompt Learning for Egocentric Action Recognition
Huaihai Lyu, Chaofan Chen, Yuheng Ji, Changsheng Xu
ACM MM 2025
EgoPrompt is a prompt-learning framework for egocentric action recognition that jointly models verbs and nouns by capturing their semantic relationships. It introduces a Unified Prompt Pool and a Diverse Pool Criteria to encourage rich, disentangled representations. EgoPrompt achieves state-of-the-art performance on Ego4D, EPIC-Kitchens, and EGTEA across various generalization benchmarks.
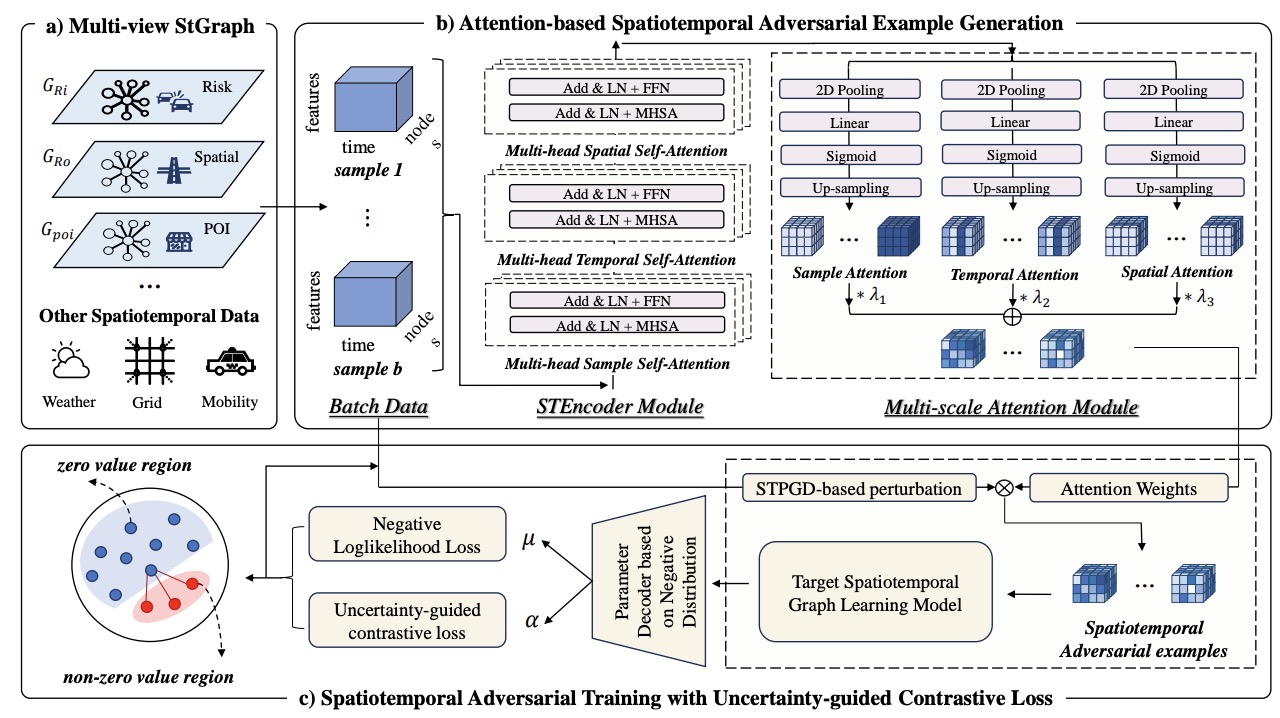
Songran Bai, Yuheng Ji, Yue Liu, Xingwei Zhang, Xiaolong Zheng, Daniel Dajun Zeng
AAAI 2025 (Oral)
Spatiotemporal graph learning under zero-inflated distribution is vital for urban risk management but is susceptible to adversarial attacks. Traditional adversarial training increases performance disparities between classes. We propose the MinGRE framework to reduce these disparities and enhance robustness.
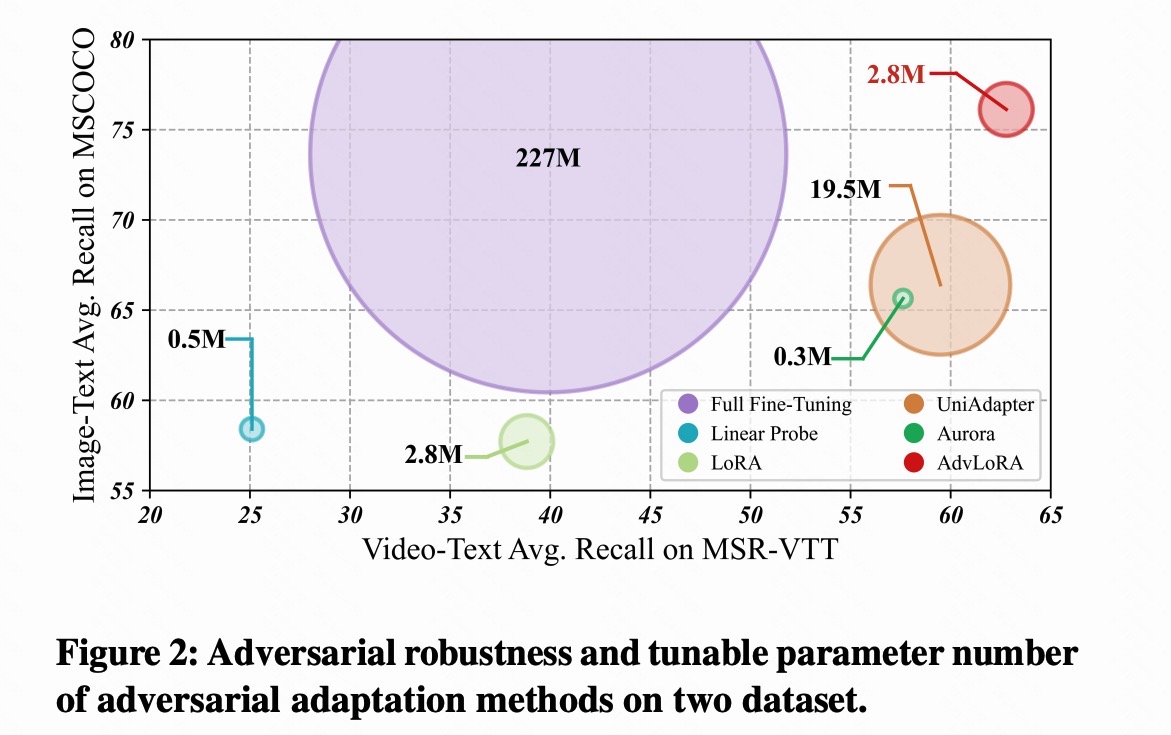
Enhancing Adversarial Robustness of Vision-Language Models through Low-Rank Adaptation
Yuheng Ji*, Yue Liu*, Zhicheng Zhang, Zhao Zhang, Yuting Zhao, Xiaoshuai Hao, Gang Zhou, Xingwei Zhang, Xiaolong Zheng
First Author, ICMR 2025
We propose a parameter-efficient adversarial adaptation method named AdvLoRA by low-rank adaptation to improve the robustness of vision-language models.
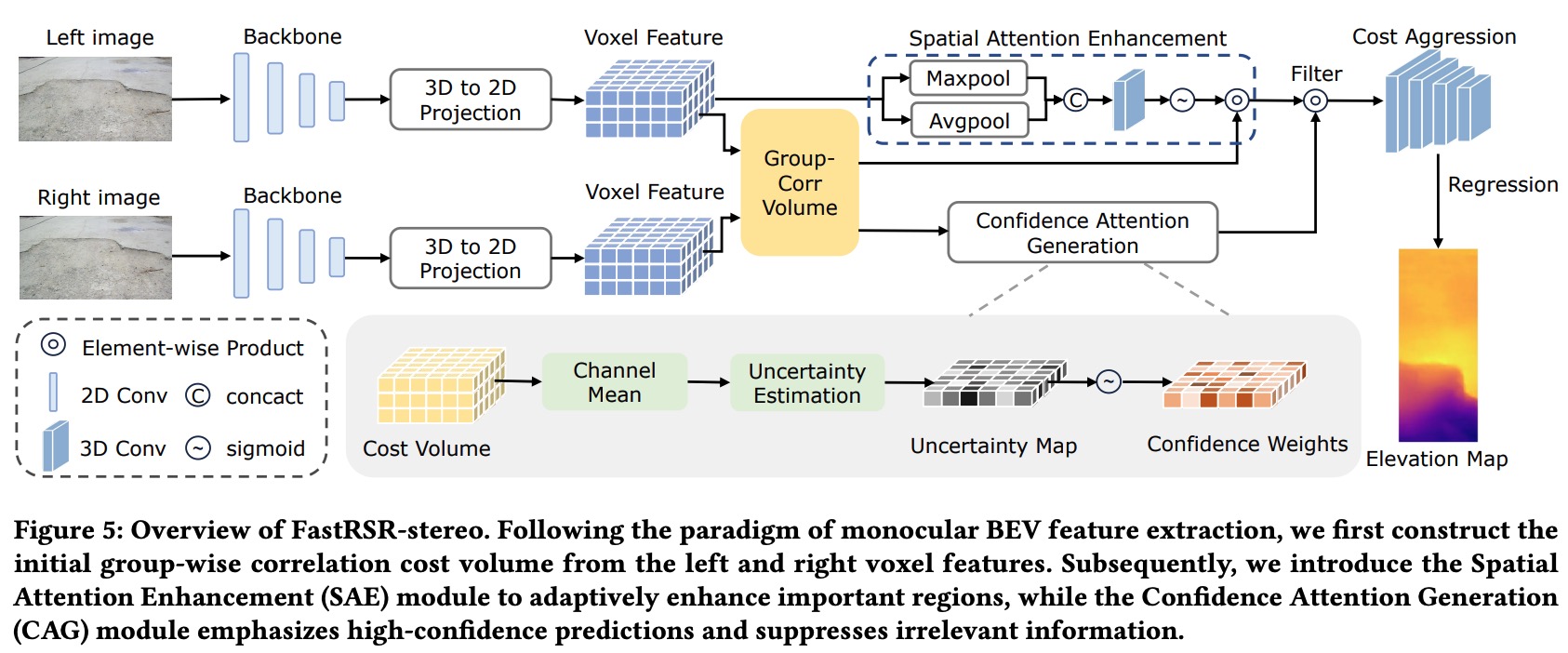
FastRSR: Efficient and Accurate Road Surface Reconstruction from Bird’s Eye View
Yuting Zhao*, Yuheng Ji*, Xiaoshuai Hao, Shuxiao Li
First Author, ACM MM 2025
Road surface reconstruction is crucial for autonomous driving, enabling the understanding of road surface conditions. We present two BEV-based RSR models: FastRSR-mono and FastRSR-stereo, offering superior efficiency and accuracy across elevation error and processing speed.
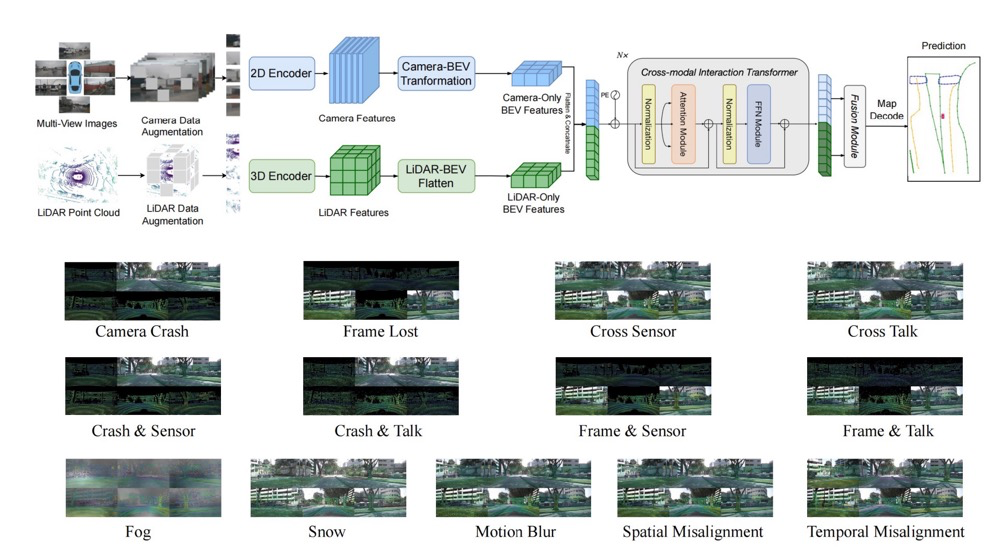
What Really Matters for Robust Multi-Sensor HD Map Construction?
Xiaoshuai Hao, Yuting Zhao, Yuheng Ji, Luanyuan Dai, Shuai Cheng, Rong Yin
IROS 2025 (Oral)
This paper enhances HD map construction robustness via data augmentation, a new fusion module, and modality dropout. It improves performance under sensor corruptions and achieves SOTA accuracy on NuScenes.
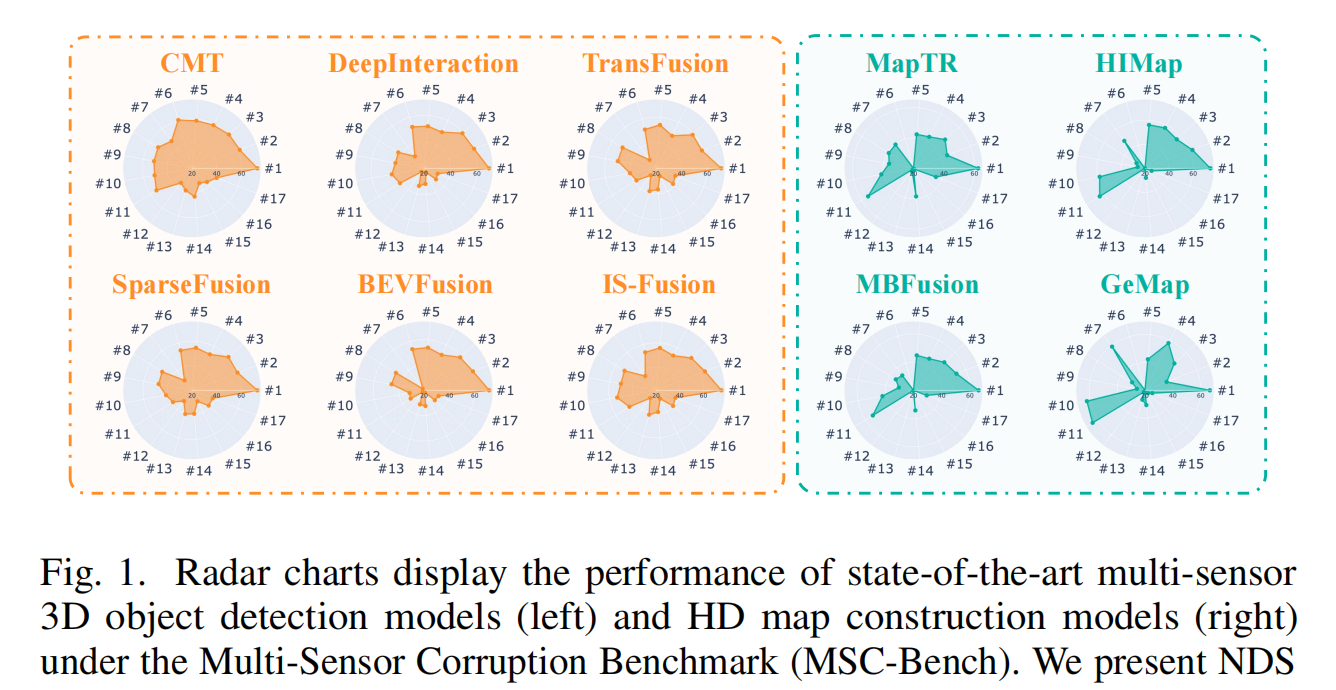
MSC-Bench: Benchmarking and Analyzing Multi-Sensor Corruption for Driving Perception
Xiaoshuai Hao, Guanqun Liu, Yuting Zhao, Yuheng Ji, Mengchuan Wei, Haimei Zhao, Lingdong Kong, Rong Yin, Yu Liu
ICME 2025 (Oral)
This work introduces the Multi-Sensor Corruption Benchmark (MSC-Bench), the first comprehensive benchmark aimed at evaluating the robustness of multi-sensor autonomous driving perception models against various sensor corruptions.
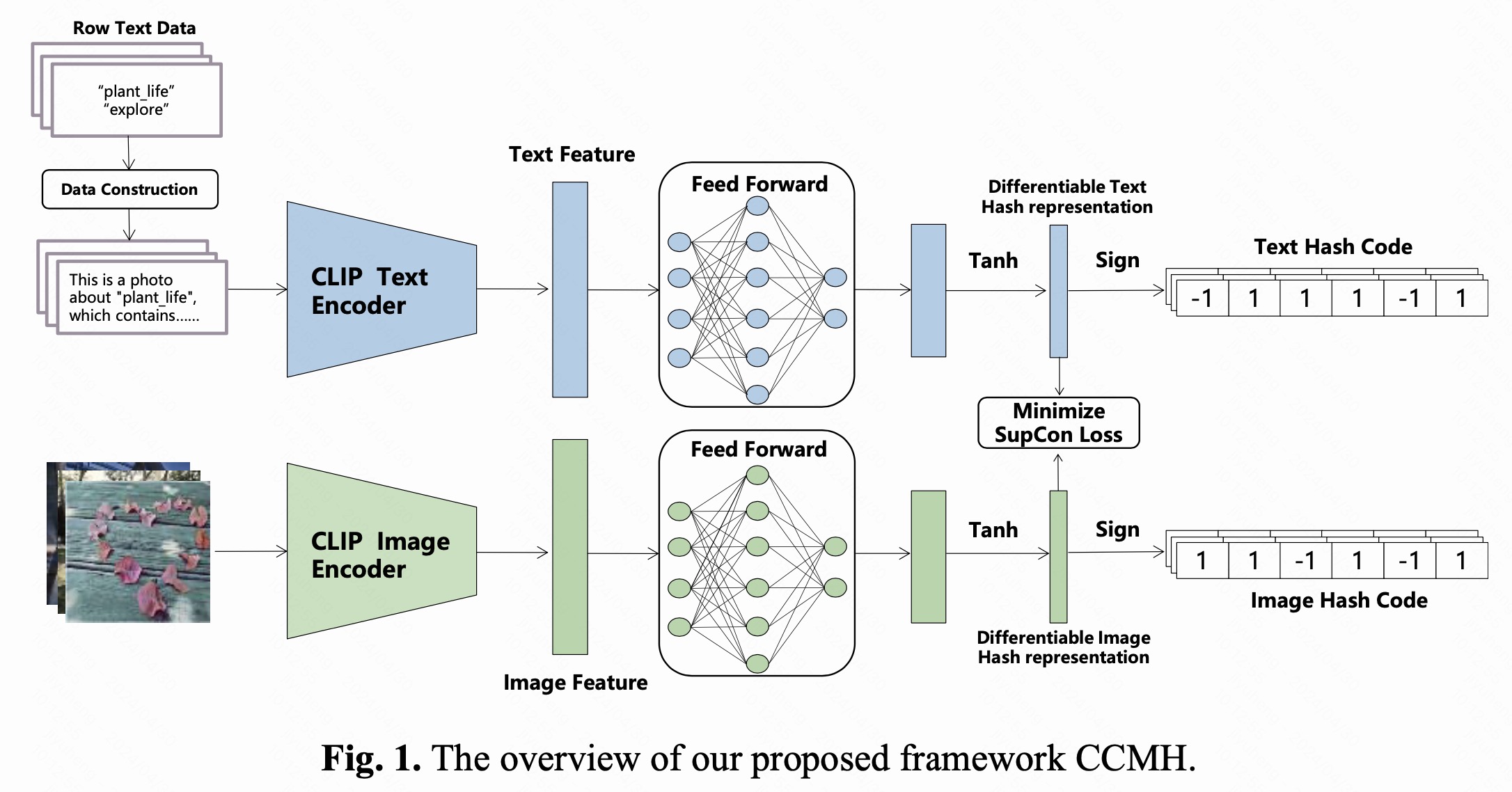
Yuheng Ji*, Xingwei Zhang*, Gang Zhou, Xiaolong Zheng, Daniel Dajun Zeng
First Author, The 11st C2 China 2023 (Outstanding Paper Award)
We propose a cross-modal hashing framework called CCMH (CLIP-based Cross-Modal Hashing), which facilitates the transferability of a well-trained real-value semantic subspace to a hash semantic subspace.
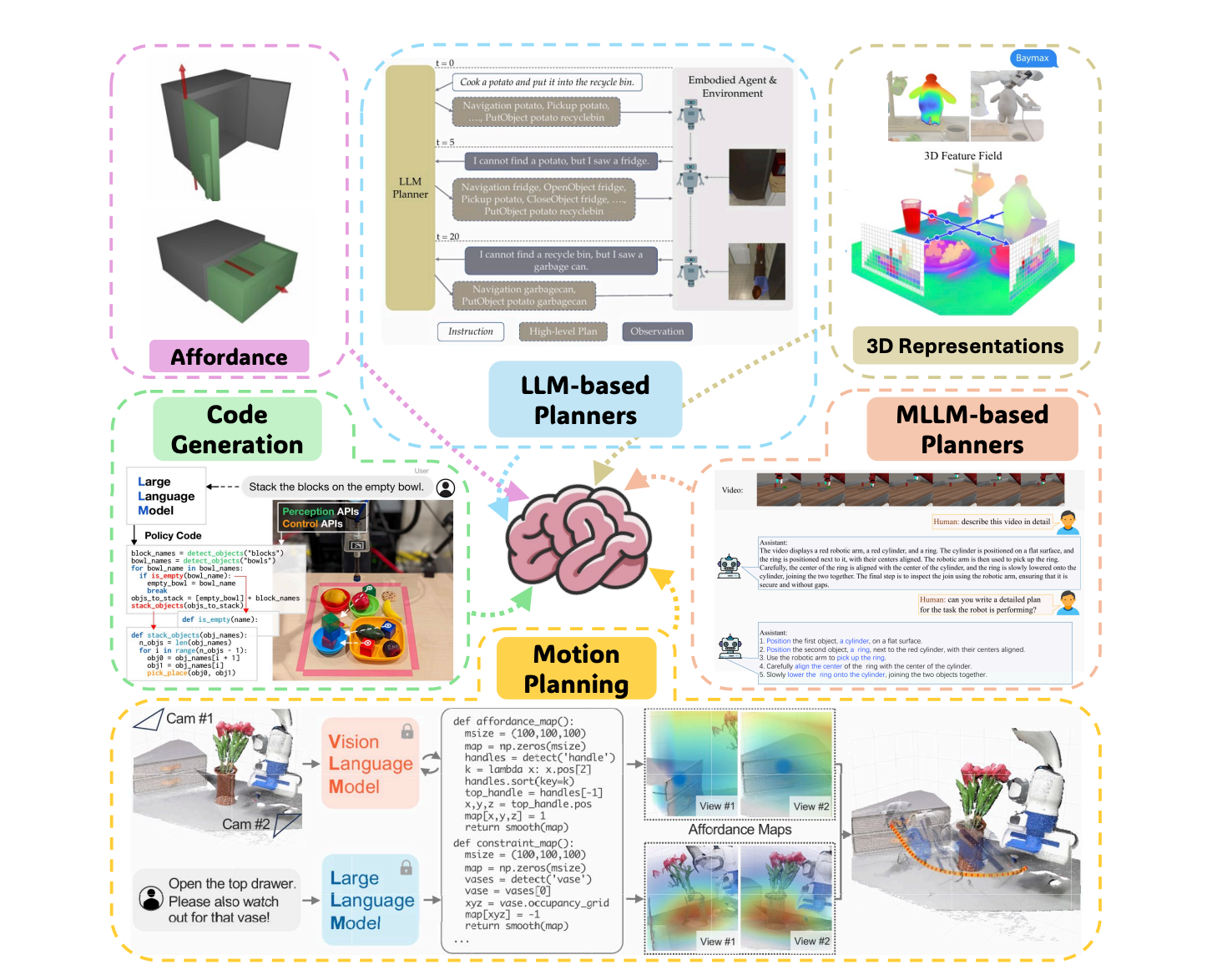
Embodied Robot Manipulation in the Era of Foundation Models: Planning and Learning Perspectives
Shuanghao Bai, Wenxuan Song, Jiayi Chen, Yuheng Ji, Zhide Zhong, Jin Yang, Han Zhao, Wanqi Zhou, Zhe Li, Pengxiang Ding, Cheng Chi, Chang Xu, Xiaolong Zheng, Donglin Wang, Haoang Li, Shanghang Zhang, Badong Chen
ArXiv 2025
This survey revisits robot manipulation in the foundation-model era through a unified two-level abstraction: high-level planning and low-level control. It organizes algorithmic design choices, summarizes representative methods, and highlights open challenges in scalability, data efficiency, multimodal physical interaction, and safety.
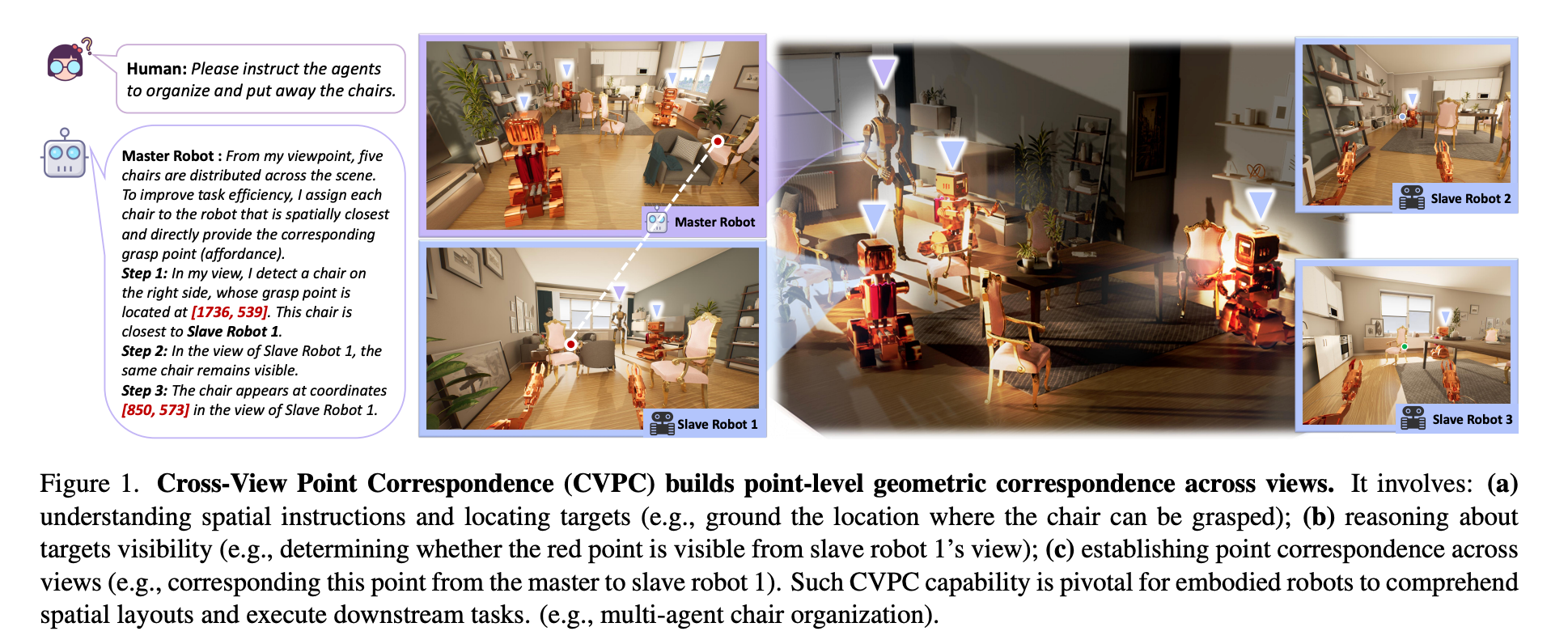
Towards Cross-View Point Correspondence in Vision-Language Models
Yipu Wang*, Yuheng Ji*, Yuyang Liu, Enshen Zhou, Ziqiang Yang, Yuxuan Tian, Ziheng Qin, Yue Liu, Huajie Tan, Cheng Chi, Zhiyuan Ma, Daniel Dajun Zeng, Xiaolong Zheng
First Author, ArXiv 2025
This work introduces the Cross-View Point Correspondence task and CrossPoint-Bench to evaluate point-level cross-view grounding in VLMs. It further proposes CrossPoint-378K and CroPond to improve fine-grained correspondence accuracy for embodied affordance-centric interaction.
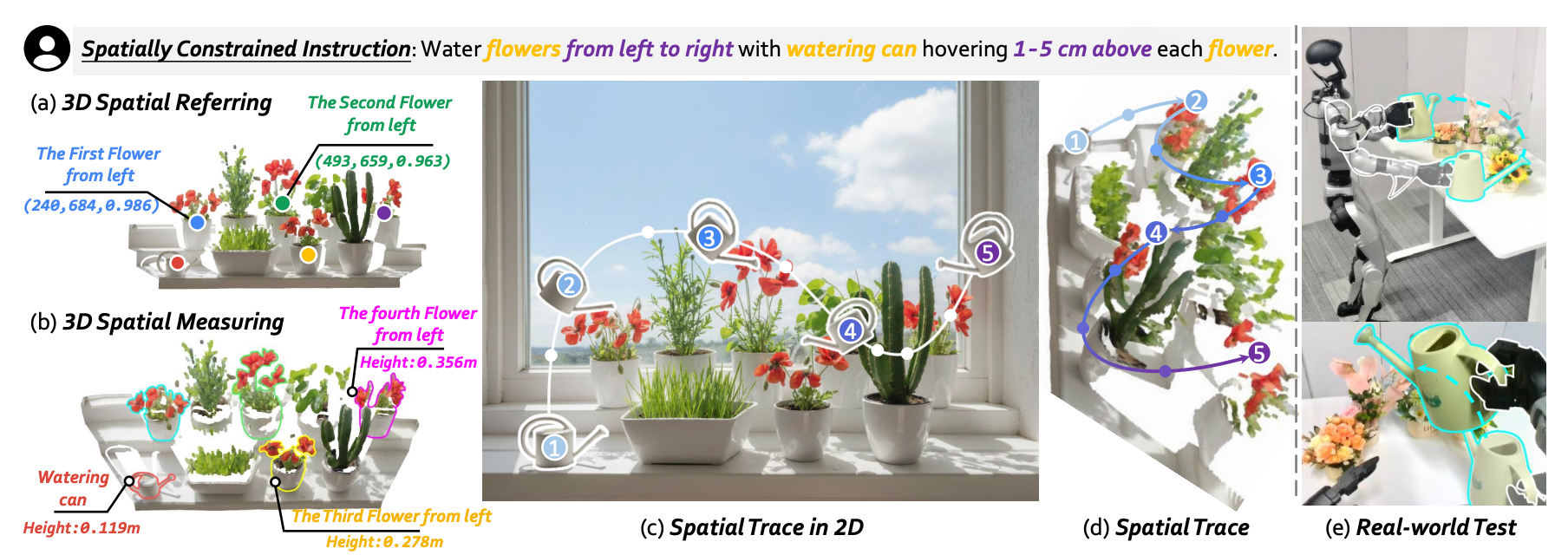
RoboTracer: Mastering Spatial Trace with Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
Enshen Zhou, Cheng Chi, Yibo Li, Jingkun An, Jiayuan Zhang, Shanyu Rong, Yi Han, Yuheng Ji, Mengzhen Liu, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Lu Sheng, Shanghang Zhang
ArXiv 2025
RoboTracer targets metric-grounded multi-step spatial tracing for robotics by combining 3D-aware supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement fine-tuning under metric-sensitive process rewards. It improves spatial referring, measuring, and long-horizon trace generation in real-world embodied settings.

RoboMirror: Understand Before You Imitate for Video to Humanoid Locomotion
Zhe Li, Cheng Chi, Boan Zhu, Yangyang Wei, Shuanghao Bai, Yuheng Ji, Yibo Peng, Tao Huang, Pengwei Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, S.-H. Gary Chan, Chang Xu, Shanghang Zhang
ArXiv 2025
RoboMirror proposes a retargeting-free video-to-humanoid-locomotion pipeline under the principle of “understand before imitate”. By extracting visual motion intent from egocentric/third-person videos and conditioning diffusion policies, it narrows the gap between visual understanding and control.
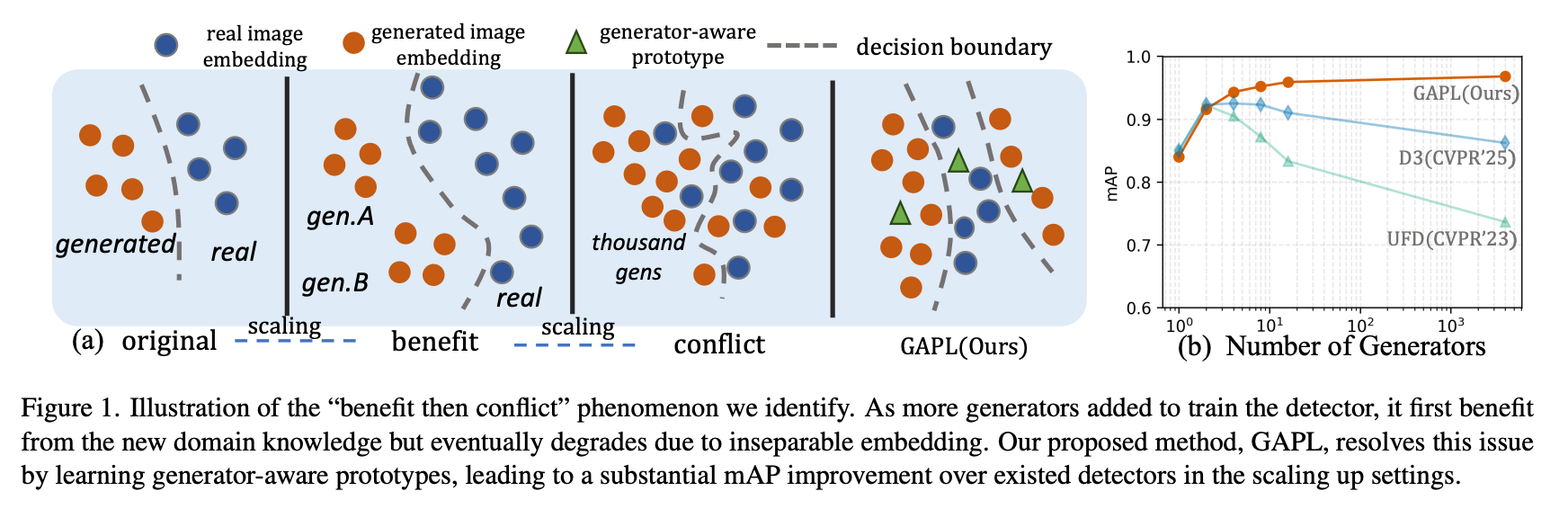
Scaling Up AI-Generated Image Detection via Generator-Aware Prototypes
Ziheng Qin*, Yuheng Ji*, Renshuai Tao, Yuxuan Tian, Yuyang Liu, Yipu Wang, Xiaolong Zheng
First Author, CVPR 2026
This work studies the scaling challenge of universal AI-generated image detection and proposes Generator-Aware Prototype Learning (GAPL). By combining canonical forgery prototypes with a two-stage low-rank adaptation strategy, it improves robustness across diverse generators.
💼 Experience
- PhD candidate student @ Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Automation (CASIA), supervised by Prof. Xiaolong Zheng
- Visiting student @ Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI), supervised by Prof. Shanghang Zhang, Dr. Pengwei Wang and Dr. Cheng Chi
- Remote visiting student @ National University of Singapore (NUS), working with Ph.D. Yue Liu
- Bachelor of engineering @ Northeastern University, supervised by Prof. Miao Fang
🤝 Services
- Reviewer for CVPR, ICLR, ICML, ICMR, ICME, AAAI
🏆 Awards
- [2025] China National Scholarship for Master’s Degree Students, National Award
- [2024] Merit Student, UCAS, School Award
- [2023] Outstanding Graduates, Provincial Award
- [2022] Recommendation for admission to CASIA
- [2022] Merit Student, Provincial Award
- [2022] China National Scholarship for Undergraduate Student, National Award
- [2021] China National Scholarship for Undergraduate Student, National Award
- [2020] China National Scholarship for Undergraduate Student, National Award
- [2019-2023] Scholarships, School Award
📎 Others
- [2024] 冀昱衡, 张曌, 郑晓龙, “大模型微调中的低秩性,” 中国指挥与控制学会通讯 55 (1), 44-49.
- [2023] 冀昱衡, 张兴伟, 郑晓龙, “基于多模态预训练的跨模态检索算法研究,” 中国指挥与控制学会通讯 46 (4), 10-16.
- [2023] 一种基于多模态预训练的跨模态哈希检索系统,发明专利,第一发明人
- [2023] 一种基于图神经网络的信用卡欺诈检测系统,发明专利,第一发明人
- [2023] 一种针对检索模型的在线隐私保护系统,发明专利,第二发明人
- [2022] 一种基于新闻主题句的文本情感分类系统,发明专利,第二发明人
📌 Participation in Research Projects
在攻读硕博期间参与了以下项目研究,主要负责项目中跨模态信息语义融合与理解等专题研究工作:
- 新技术驱动的复杂社会系统管理, 国家杰出青年科学基金项目
- 基于多模态数据融合的智能社会风险预警研究, 国家自然科学基金重点项目
- 跨模态多语言大数据驱动的社会风险感知与理解, 2030—“新一代人工智能”重大项目


